

This first orbital forms a shell around the nucleus and is assigned a principal quantum number (n) of n=1.
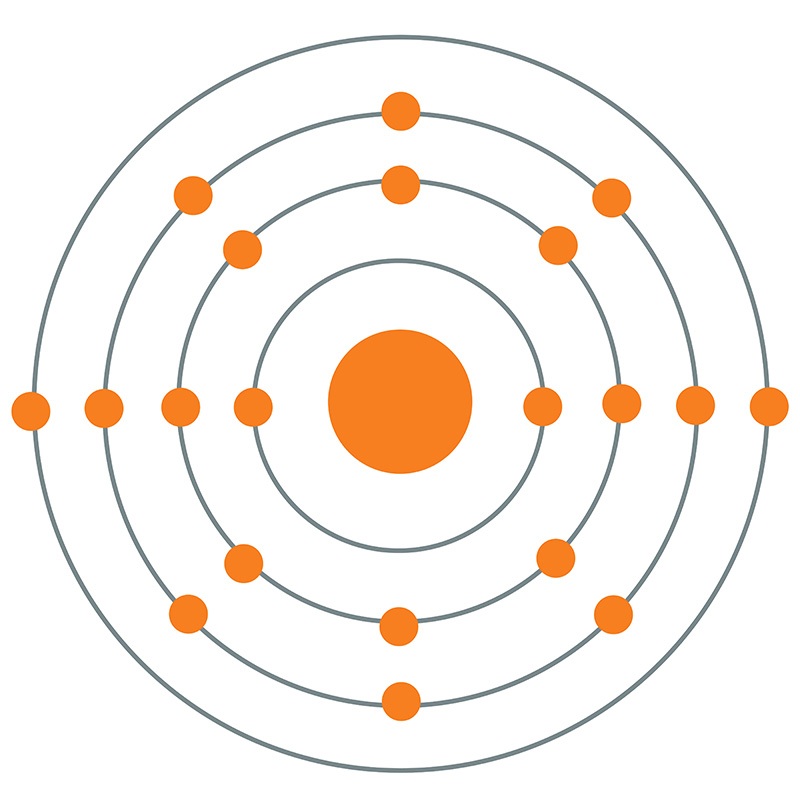
In the Bohr model, the most stable, lowest energy level is found in the innermost orbit. To account for the observed properties of hydrogen, Bohr proposed that electrons existed only in certain orbits and that, instead of traveling between orbits, electrons made instantaneous quantum leaps or jumps between allowed orbits. In addition, physicist James Clark Maxwell ’s influential studies on electromagnetic radiation (light) predicted that an electron orbiting around the nucleus according to Newton ’s laws would continuously lose energy and eventually fall into the nucleus. Spectroscopic experiments, however, showed that hydrogen atoms produced only certain colors when heated. This predicted that when, for example, a hydrogen atom was heated, it should produce a continuous spectrum of colors as it cooled because its electron, moved away from the nucleus by the heatenergy, would gradually give up that energy as it spiraled back closer to the nucleus. The classical model of the atom allowed electrons to orbit at any distance from the nucleus.

During this time Bohr developed his model of atomic structure.īefore Bohr, the classical model of the atom was similar to the Copernican model of the solar system where, just as planets orbit the sun, electrically negative electrons moved in orbits about a relatively massive, positively charged nucleus. After graduation, Bohr worked in England with Thomson and subsequently with Rutherford. While working on his doctoral dissertation at Copenhagen University, Bohr studied physicist Max Planck ’s (1858 –1947) quantum theory of radiation. Thomson and Ernest Rutherford by incorporating quantum theory. Published in 1913, Bohr ’s model improved the classical atomic models of physicists J. The Bohr model of atomic structure was developed by Danish physicist and Nobel laureate Niels Bohr (1885 –1962).


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
